Carbohydrate
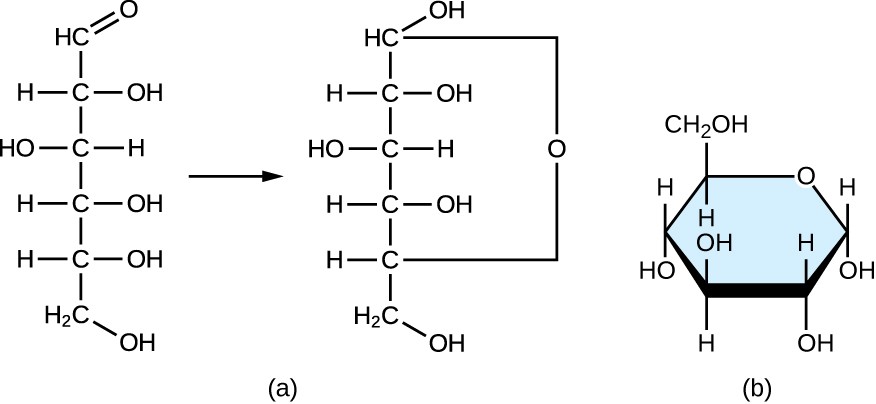
The stoichiometric formula of carbohydrates is (CH2O)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. "Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods" ((Rye et al., 2017p.67). "The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6. In humans, glucose is an important source of energy" (Rye et al., 2017, p.68). Glucose is essential for the normal functioning of the brain.
Lipid
Fats are also called triacylglycerols or triglycerides because of their chemical structure, “a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyls (OH) groups. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl group is attached, hence the name “fatty acid” (Rye et al., 2017, 76). Omega fatty acid is essential fatty acids are fatty acids required but not synthesized by the human body (Rye et al., 2017, p.79). Omega fatty acid Reduces the risk of developing liver cancer and colon cancer (MacLean et al., 2006).

Protein
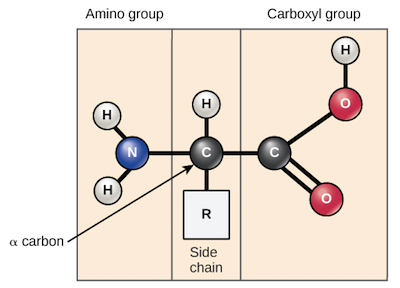
Amino acids are the monomers that makeup proteins, consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH). There are 20 amino acids present in proteins, but ten of these are considered essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them obtained from the diet. (Rye et al., 2017). Glutamic acid is one of the excitatory neurotransmitters in the nervous system and plays a vital role in higher brain functions such as memory and learning (Danbolt, 2001).
Nucleic acid
DNA and RNA are made up of monomers known as nucleotides, and the nucleotides combine with each other to form a polynucleotide, DNA, or RNA. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose (five-carbon) sugar, and a phosphate group, each nitrogenous base in a nucleotide is attached to a sugar molecule, which is attached to one or more phosphate groups (Rye et al., 2017). DNA is the genetic material found in all living organisms, ranging from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals (Rye et al., 2017). RNA is usually single-stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds, carry the message from DNA, which controls all of the cellular activities in a cell (Rye et al., 2017).

References
Danbolt, N. C. (2001). Glutamate uptake. Progress in neurobiology, 65(1), 1-105. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301008200000678
MacLean, C. H., Newberry, S. J., Mojica, W. A., Khanna, P., Issa, A. M., Suttorp, M. J., ... & Morton, S. C. (2006). Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cancer risk: a systematic review. Jama, 295(4), 403-415. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/202260
Rye, C., Wise, R., Jurukovski, V., Desaix, J., Choi, J., & Avissar ,Y. (2017). Biology. OpenStax College, Rice University. Retrieved from https://my.uopeople.edu/pluginfile.php/1097682/mod_page/content/7/PSYCTextCh_1-4.pdf
| Across 1. protein that acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions 6. component of fat molecule 8. acidic group in amino acids 9. monosaccharide commonly found in fruit 11. fatty acid with hydrogens in different planes 12. monomer subunit of protein 14. major constituent of plasma membrane 17. fatty acid containing no double bonds 18. nucleic acid found only in RNA 19. bond formed between two amino acids 20. number of amino acids |
Down 2. single unit of a polymer 3. structure of polypeptide chain that contains beta sheets 4. provides structural support in plant cells 5. type of bond between monosaccharides in a chain 7. used for long term energy storage 10. biological macromolecule with a ratio of 1 C:2 H:1 O 13. sugar backbone of DNA 15. type of reaction used to form polymers 16. adenine and guanine are this type of nucleotide |




댓글